Data Branching
In SynxDB Elastic, data branching is a powerful feature that allows users to create a fully functional copy of an existing table at a very low cost. It works similarly to the “branch” concept in the Git version control system.
What it is: manage data like Git
The data branching feature allows you to quickly create a new table (for example, t2) based on an existing one (for example, t1). This creation process is highly efficient because it does not initially copy any physical data. Instead, the newly created branch table shares the same set of underlying data blocks with the original table.
When you perform a write operation (such as INSERT, UPDATE, DELETE) on any branch table, the system uses a “Copy-on-Write” mechanism. It only creates new, independent data blocks for the branch where the changes occur, while the original data remains untouched.
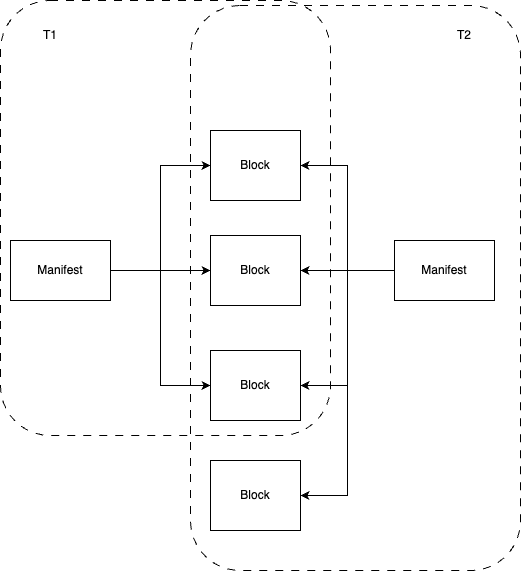
The figure above shows t2 as a branch of t1. Initially, they share the same data blocks. When t2 is written to, it creates its own new data blocks.
What it’s for: efficient, isolated, zero-cost data snapshots
Using the data branching feature offers the following core advantages:
Instantaneous creation, cost savings: Creating a branch is almost instantaneous because it avoids large-scale data copying, which significantly saves time and storage space.
Safe and isolated experimental environment: Any operations performed on a branch table (including modifying, deleting data, or even
TRUNCATE) do not affect the original table or other branches. This provides a perfect sandbox environment for data experiments and development without worrying about damaging production data.Simplified data version management: You can create different data branches for different tasks (such as daily reports, data cleansing, machine learning training, etc.), making it easy to manage multiple versions of your data.
Use cases
Data branching is ideal for the following scenarios:
ETL/ELT development and testing: You can create a branch from a production data table and then develop and debug your data transformation scripts on that branch. If something goes wrong, you can simply delete the branch without any impact on the production data.
Data analysis and scientific exploration: Data analysts can create a private data branch for themselves. On this branch, they can freely add columns, clean data, and perform various exploratory analyses without interfering with the team’s shared original dataset.
“What-if” analysis: Create a branch based on current data, and then simulate the impact of business changes (such as price adjustments, marketing campaigns, etc.) in the branch. This makes complex data forecasting and modeling both safe and efficient.
Software development and continuous integration (CI/CD): In the application testing process, a database branch can be automatically created for each test task. This ensures that each test runs in a clean, isolated environment, avoiding interference between tests.
How to use
Create a branch
BRANCHING new_table_name FROM existing_table_name;
Example: Suppose there is a production table named sales_prod, and you want to create a branch for quarterly report analysis.
BRANCHING sales_q2_report FROM sales_prod;
After execution, a new table named sales_q2_report will be created. Initially, it shares all data with sales_prod. Subsequently, all modifications to sales_q2_report will be independent of sales_prod.
Considerations
Table type limitation: This feature is only supported for
storageamtype tables.Automatic background management: SynxDB Elastic automatically tracks the reference status of data blocks in the background. When you use commands like
DROP TABLE,TRUNCATE, orVACUUM, the system intelligently determines if a data block is still referenced by other branches and ensures that data is only deleted when there are no more references, thus guaranteeing data safety. Users do not need to worry about this internal mechanism and can operate branch tables just like regular tables.Affected commands: The
BRANCHING,DROP TABLE,TRUNCATE TABLE, andVACUUMcommands interact with the branch’s reference counting system to ensure data consistency and integrity.